Using a novel polymerization process, MIT chemical engineers have created a new material that is stronger than steel and as light as plastic, and can be easily manufactured in large quantities.
The new material is a two-dimensional polymer that self-assembles into sheets, unlike all other polymers, which form one-dimensional, spaghetti-like chains. Until now, scientists had believed it was impossible to induce polymers to form 2D sheets.
Such a material could be used as a lightweight, durable coating for car parts or cell phones, or as a building material for bridges or other structures, says Michael Strano, the Carbon P. Dubbs Professor of Chemical Engineering at MIT and the senior author of the new study.
“We don’t usually think of plastics as being something that you could use to support a building, but with this material, you can enable new things,” he says. “It has very unusual properties and we’re very excited about that.”
The researchers have filed for two patents on the process they used to generate the material, which they describe in a paper published in Nature on February 2, 2022. MIT postdoc Yuwen Zeng is the lead author of the study.
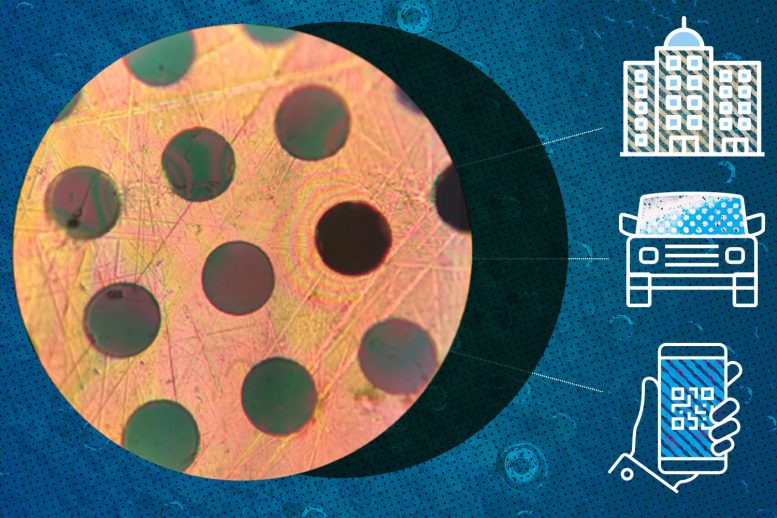
The new material is a two-dimensional polymer that self-assembles into sheets and could be used as a lightweight, durable coating for car parts or cell phones, or as a building material for bridges or other structures. Credit: polymer film courtesy of the researchers; Christine Daniloff, MIT
Two dimensions
Polymers, which include all plastics, consist of chains of building blocks called monomers. These chains grow by adding new molecules onto their ends. Once formed, polymers can be shaped into three-dimensional objects, such as water bottles, using injection molding.
Polymer scientists have long hypothesized that if polymers could be induced to grow into a two-dimensional sheet, they should form extremely strong, lightweight materials. However, many decades of work in this field led to the conclusion that it was impossible to create such sheets. One reason for this was that if just one monomer rotates up or down, out of the plane of the growing sheet, the material will begin expanding in three dimensions and the sheet-like structure will be lost.
However, in the new study, Strano and his colleagues came up with a new polymerization process that allows them to generate a two-dimensional sheet called a polyaramide. For the monomer building blocks, they use a compound called melamine, which contains a ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms. Under the right conditions, these monomers can grow in two dimensions, forming disks. These disks stack on top of each other, held together by hydrogen bonds between the layers, which make the structure very stable and strong.
“Instead of making a spaghetti-like molecule, we can make a sheet-like molecular plane, where we get molecules to hook themselves together in two dimensions,” Strano says. “This mechanism happens spontaneously in solution, and after we synthesize the material, we can easily spin-coat thin films that are extraordinarily strong.”
Because the material self-assembles in solution, it can be made in large quantities by simply increasing the quantity of the starting materials. The researchers showed that they could coat surfaces with films of the material, which they call 2DPA-1.
“With this advance, we have planar molecules that are going to be much easier to fashion into a very strong, but extremely thin material,” Strano says.
Light but strong
The researchers found that the new material’s elastic modulus — a measure of how much force it takes to deform a material — is between four and six times greater than that of bulletproof glass. They also found that its yield strength, or how much force it takes to break the material, is twice that of steel, even though the material has only about one-sixth the density of steel.
Matthew Tirrell, dean of the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering at the University of Chicago, says that the new technique “embodies some very creative chemistry to make these bonded 2D polymers.”
“An important aspect of these new polymers is that they are readily processable in solution, which will facilitate numerous new applications where high strength to weight ratio is important, such as new composite or diffusion barrier materials,” says Tirrell, who was not involved in the study.
Another key feature of 2DPA-1 is that it is impermeable to gases. While other polymers are made from coiled chains with gaps that allow gases to seep through, the new material is made from monomers that lock together like LEGOs, and molecules cannot get between them.
“This could allow us to create ultrathin coatings that can completely prevent water or gases from getting through,” Strano says. “This kind of barrier coating could be used to protect metal in cars and other vehicles, or steel structures.”
Strano and his students are now studying in more detail how this particular polymer is able to form 2D sheets, and they are experimenting with changing its molecular makeup to create other types of novel materials.








